Definition: Theobromine
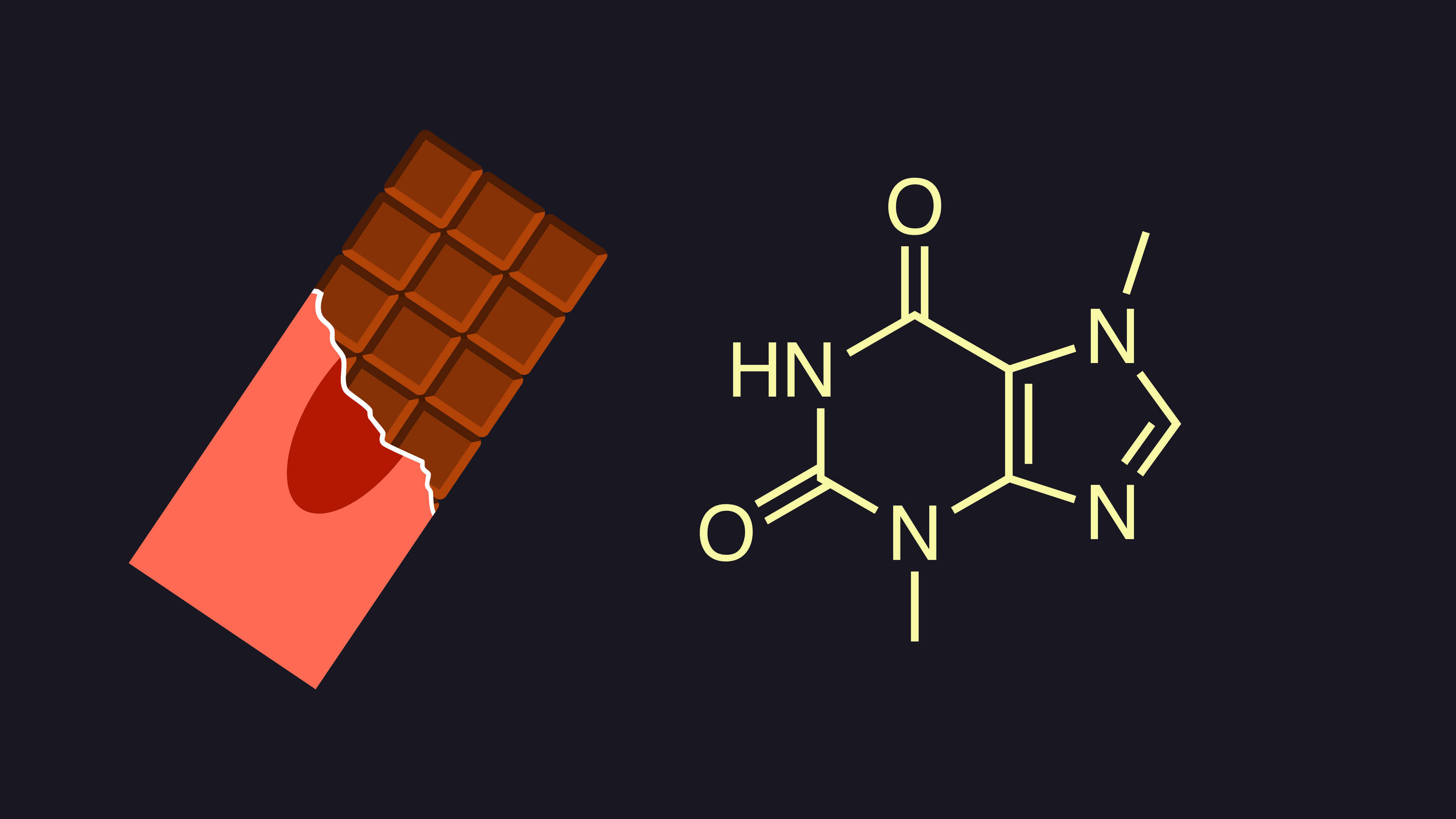
What is theobromine?
The term theobromine comes from the Greek theos (God) and broma (food), literally "food of the gods". This may seem a strange name for a chemical substance, but it reflects the historical importance attached to cocoa and the foods derived from it, such as chocolate.
Theobromine belongs to the methylxanthine family, which also includes caffeine, famous for its presence in coffee and soft drinks, for example. Structurally, they are very similar and share certain pharmacological properties, although their respective effects and concentrations vary widely according to food sources.
Where does it come from?
The main source of theobromine is undoubtedly cocoa. Lesser quantities are found in tea, as well as in certain exotic fruits such as guarana and mate. Even within these plants, theobromine concentration can vary considerably according to growing conditions, variety, age and environment.
A stimulating effect on the body
The pharmacological effects of theobromine are largely related to those of methylxanthines in general. In particular, it has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system, as well as on the cardiovascular system and muscles.
Comparison with caffeine
However, it's important to note that its stimulating effect is less powerful than that of caffeine. For example, a cup of cocoa contains around 200 mg of theobromine, while a cup of coffee generally contains between 60 and 120 mg of caffeine. The effects of these two substances cannot therefore be compared on an equivalent basis.
The other major difference between the two molecules is their duration of action: caffeine's half-life is generally around three to seven hours, compared with six to ten hours for theobromine. Theobromine is therefore active in the body for longer, even if its effects are less intense.
Effects on mood
The presence of theobromine in chocolate partly explains the euphoric effects often reported. In fact, it acts directly on our brain by increasing the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, which is responsible for the sensation of well-being and pleasure. It also appears to inhibit the action of certain enzymes, such as phosphodiesterases, which can have a relaxing effect on the body.
Theobromine and sport
Given its vasodilatory and relaxing properties, theobromine could also have a positive influence on sport. Here again, the effect is not comparable to that of caffeine, but rather a potential improvement in blood circulation and oxygen transport to active muscles. Some athletes claim that consuming cocoa or dark chocolate before exercise improves performance.
Side effects and contraindications
Although less intense than caffeine overall, theobromine can nevertheless cause discomfort in sensitive individuals, particularly in the digestive tract (bloating, gas) and the cardiovascular system (palpitations, tachycardia). Consumption should therefore be moderated in cases of proven intolerance or other predispositions.
Why is chocolate toxic for animals?
It's important to remember that theobromine is extremely toxic to some animals, particularly dogs and cats. In these species, it can cause serious symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, agitation, convulsions or hyperthermia at relatively low doses. Because of the high theobromine content of chocolate, it's vital to keep this food out of the reach of our four-legged friends.
Theobromine and dental health
To end on a more positive note, several studies have demonstrated the beneficial effect of theobromine on oral health. It appears to be able to inhibit certain bacteria responsible for plaque formation, as well as strengthening enamel thanks to its calcium and phosphorus content.
- The main source of theobromine is cocoa,
- It has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system, less powerful than caffeine,
- theobromine could also have a positive influence on sport,
- In animals such as dogs and cats, theobromine can be extremely toxic,
- Theobromine is also said to have a beneficial effect on oral health.





